What is Marcus Gunn syndrome, in which the eyelid moves with the jaw: Understanding risks and inheritance
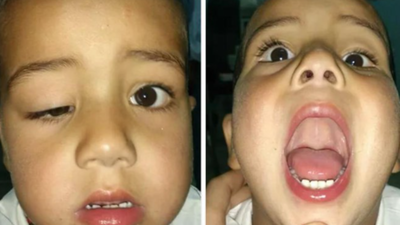
Marcus Gunn Syndrome, or Marcus Gunn jaw winking ptosis, is a rare congenital disorder that presents as a droopy eyelid invariably lifting or winking to the rhythm of jaw movements. It was first discovered by British eye specialist Robert Marcus Gunn in 1883 and is observed to occur in 5 percent of children born with ptosis, or droopy upper lid of the eye. Such abnormal lid movement is bound to draw attention, especially among infants when they feed or chew. Read on to know more about this rare condition
Understanding the condition
The characteristic feature of Marcus Gunn Syndrome consists of synkinesis, which can be described as the inappropriate innervation between nerves responsible for the control of the jaw and the control of the eyelid. Under normal conditions, the levator palpebrae superioris muscle, which elevates the superior eyelid, would be innervated by the oculomotor nerve, the third pair of nerves emanating from the brain, cranial nerve III. While the jaw muscles, including the external pterygoid, would be innervated by the trigeminal nerve, the fifth pair of nerves emanating from the brain, the fifth nerve, cranial nerve V.

This causes one-lateral ptosis, in which one eyelid droops while the jaw is in repose but moves too high during these motions. The wink can be subtle or very pronounced, even creating a vertical range of 20 mm, in which parents notice it while the child is being breastfed as the child sucks, which triggers the eyelid elevation. It is congenital, except in some acquired cases caused by injury, surgeries, or syphilis infection.
Causes of this syndrome
Marcus Gunn syndrome has been identified as a congenital disorder of the innervation of the head by experts. This congenital disease has genetic causes with complex patterns of autosomal inheritance and reduced penetrance. Some of the genetic causes associated with Marcus Gunn syndrome include mutations in the CHD7 gene or chromosomic problems due to the deletion of the 22q11.2 region. Some of the hypotheses include genetic defects in the early stages of the development of the brainstem and the loss of PRS due to coordination problems of the jaw and eyes during fetal life.It is estimated to occur in 2 to 6 percent of congenital ptosis, with no predominant gender distribution, although females are more likely to seek medical assistance for cosmetic appearance. Other complications are superior rectus palsy in 25 percent of those affected, double elevator paralysis in 25 percent, strabismus in 50 to 60 percent, and amblyopia due to visual obstructions with the drooping lid.
Symptoms and diagnosis

Aside from the jawwink ptosis, other possible conditions in children include amblyopia, anisometropia, and horizontal strabismus. Eyelid drooping falls on part of the pupils, which may affect the perception of distance or cause a condition called lazy eye if not treated. The blinking may be accentuated by turning the jaw towards the other side or from clenching or smiling.It is a diagnosis by observation. Also, they check by having the patient do jaw movements, such as masticating gum or lateral movements of the jaw. There is no lab test to verify it. Rather, they use exclusion of other conditions, such as the mimics Duane syndrome, congenital fibrosis, or Marin Amat syndrome, after ophthalmologic and motility studies, or even imaging studies as may be required. Early treatment will spare the loss of vision.
Treatment options
For mild, no treatment is necessary because most patients adapt without any functional problems. Simple observation would be adequate if vision is only minimally affected by ptosis. For severe winking or ptosis, a sphincterotomy or a levator resection is necessary to restore balance. Supermaximal levator resection can tighten the eyelid to achieve better elevation with a frontalis sling made of fascia lata or silicone.Timing is everything. Surgeries are usually delayed till the child is age 4 or older to allow the growth of the jaw to settle. Botox injection, on the other hand, gives temporary assistance to the pterygoid muscles to suppress the signals transmitted to the brain related to the jaw movements, which lasts approximately 3-4 months. Recent developments include neuromuscular training or AI support systems for facial rehabilitation.Most people have normal lives, with the cosmetic side affecting teenagers and adults. Counseling is important for psychologically assisting people who are embarrassed about the wink. Regular visits to the eye specialist will monitor for strabismus or changes in vision. Outcomes will remain excellent post-operatively with minimal rates of recurrence if attended to in time.Research is ongoing to identify genetic markers for improved prediction. Families find benefit in linking through rare disease communities. With early treatment, children skirt around complications while embracing the full potential for visual greatness. Sufferers understand that this quirky condition rarely spoils the everyday pleasures in life with poor management.